What is Inter Rater Reliability (IRR) in Data Abstraction?
Inter-Rater Reliability refers to the degree of agreement among different reviewers (abstractors) assessing the same clinical data. It is used to validate the quality of data abstraction for Core Measures and Registries. Consistent IRR scores indicate a high level of understanding and application of specifications by the abstractors, while low scores may highlight gaps that need to be addressed through targeted education or process changes.
Table of Contents
- Why is Inter-Rater Reliability Important?
- IRR Assessment Metrics: DEAR and CAAR
- Data Element Agreement Rate (DEAR)
- Category Assignment Agreement Rate (CAAR)
- When to Implement Inter-Rater Reliability Reviews
- Best Practices for Conducting IRR Assessments
- Outsourcing IRR Assessments for Optimal Results
Why is Inter-Rater Reliability Important?
Conducting regular IRR assessments is vital for several reasons:
- Ensures Data Accuracy: By comparing multiple abstractors’ interpretations, hospitals can verify the consistency and accuracy of their data entries. Learn more about the free IRR Ebook to implement best practices in your facility.
- Identifies Training Needs: If discrepancies are found, IRR assessments pinpoint where education and training are needed to ensure abstractors correctly apply guidelines.
- Maintains Compliance: IRR assessments help hospitals meet compliance requirements from organizations like The Joint Commission (TJC) and the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS).
For hospitals looking to enhance their quality teams, check out our strategies on improving quality teams.
IRR Assessment Metrics: DEAR and CAAR
Hospitals typically measure Inter-Rater Reliability using metrics such as the Data Element Agreement Rate (DEAR) and the Category Assignment Agreement Rate (CAAR). Both metrics provide insights into the accuracy of data abstraction at different levels.
Data Element Agreement Rate (DEAR)
The Data Element Agreement Rate, or DEAR, is a one-to-one comparison of consensus between the original abstractor and the re-abstractor’s findings at the data element level, including all clinical and demographic elements.
To calculate the DEAR for each data element:
- Count the number of times the original abstractor and re-abstractor agreed on the data element value across all paired records.
- Divide by the total number of paired records.
- Convert to a percentage and evaluate the score.
DEARs of 80% of better are acceptable.
DEAR results should be used to identify data element mismatches and pinpoint education opportunities for abstractors. It is also important to analyze the DEAR results for trends among mismatches – within a specific data element or for a particular abstractor – to determine if a more focused review is needed to ensure accuracy across all potentially affected charts.
Example DEAR Calculation (using a partial AMI data element list)
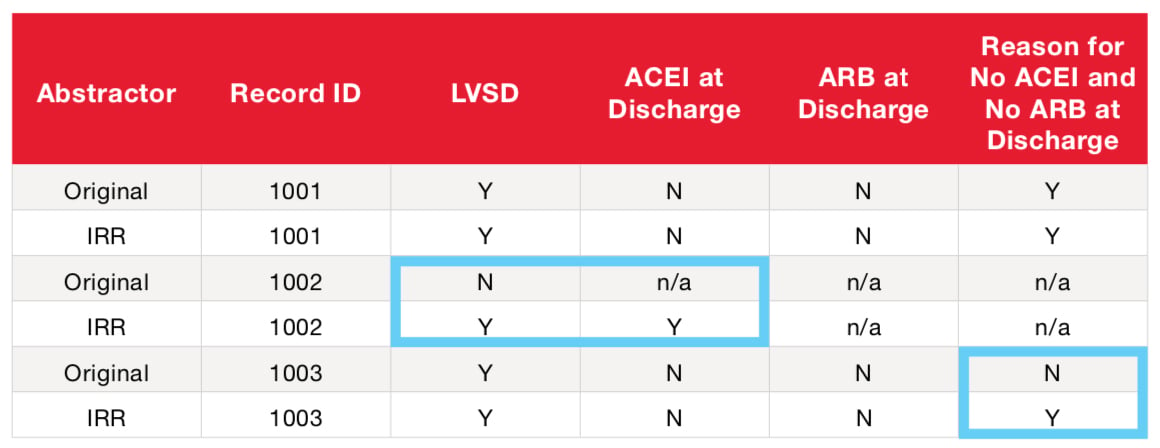
DEAR
- Add Successfully Matched Answer Values (Numerator) (2+2+2+1) = 7
- Add Total Paired Answer Values (Denominator) (3+3+2+2) = 10
- Divide Numerator by Denominator (7/10) = 70%
*n/a in the table above represents fields disabled due to skip logic.
Category Assignment Agreement Rate (CAAR)
The Category Assignment Agreement Rate, or CAAR, is the score utilized in the CMS Validation Process which affects Annual Payment Update. CAAR is a one-to-one comparison of agreement between the original abstractor and the re-abstractor’s record-level results using Measure Category Assignments (MCAs).
MCAs are algorithm outcomes that determine numerator, denominator and exclusion status and are typically expressed as A, B, C, D, E. In other words, the same numerator and denominator values reported by the original abstractor should be obtained by the second abstractor.
To calculate the CAAR:
- Count the number of times the original abstractor and re-abstractor arrived at the same MCA.
- Divide by the total number of paired MCAs.
- Express as a percentage.
A score of 75% is considered acceptable by CMS, while TJC prefers 85% or above.
CAAR results should be used to identify the overall impact of data element mismatches on the measure outcomes. CAAR mismatches can then be reviewed in conjunction with associated DEAR mismatches to foster abstractor knowledge. Remember, CAAR results are also the best predictor of CMS validation results.
Example of CAAR Calculation Within Measure Set:
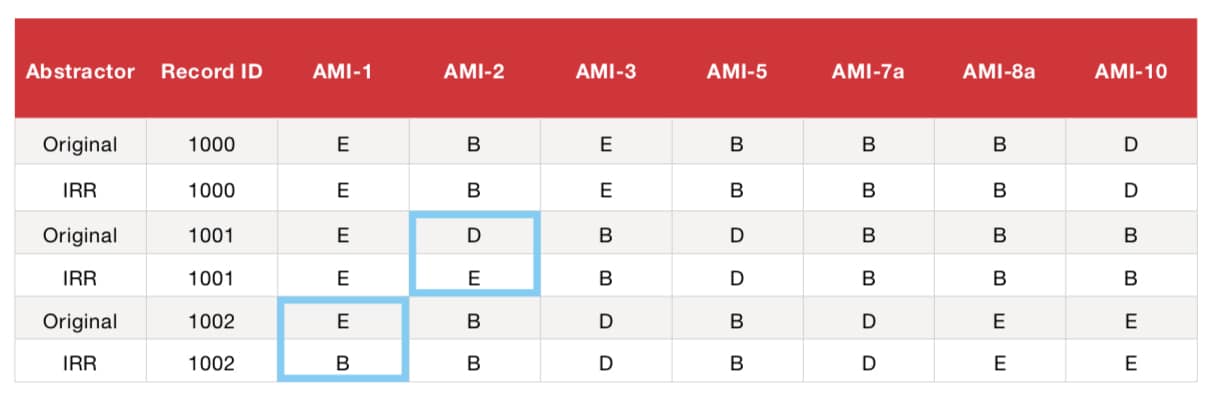
Example of CAAR Calculation Across Measure Sets:
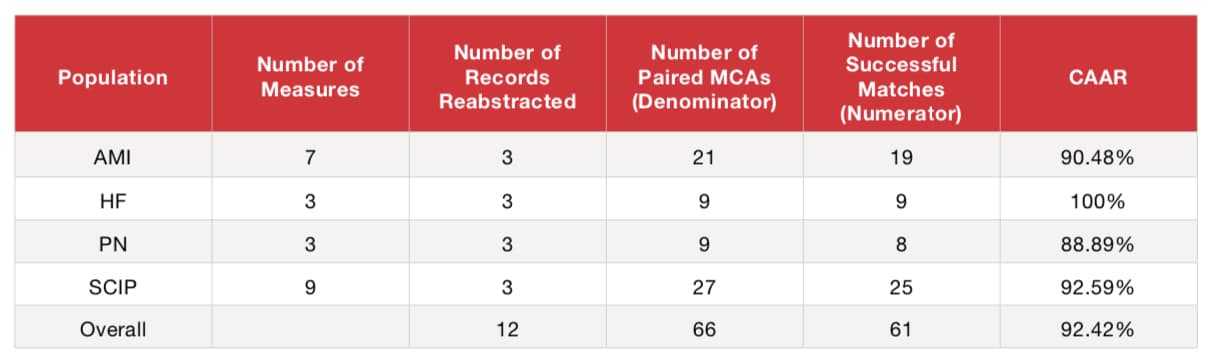
Overall CAAR
- Add Successfully Matched MCAs (Numerator) (19+9+8+25) = 61
- Add Total Paired MCAs (Denominator) (21+9+9+27) = 66
- Divide Numerator by Denominator (61/66) = 92.42%
When to Implement Inter-Rater Reliability Reviews
Incorporating Inter-Rater Reliability into your routine can reduce data abstraction errors by identifying the need for abstractor education or re-education and give you confidence that your data is not only valid, but reliable. Inter-Rater Reliability should be integrated into your hospital’s routine whenever:
- Specifications are updated.
- New abstractors are onboarded.
- New measure sets are introduced.
- Abstractors undergo performance evaluations.
Best Practices for Conducting IRR Assessments
- Select a Random Sample: Ensure that the IRR sample is randomly selected from the entire population of cases, not just those with measure failures, to get an accurate representation of data quality.
- Use an Independent Abstractor: Each case should be re-abstracted independently by a different abstractor to maintain objectivity and prevent bias.
- Compare and Identify Mismatches: The IRR abstractor inputs and compares answer values for each data element and measure category assignment to detect any discrepancies.
- Review and Correct: Review the results with the original abstractor, making necessary corrections before submission deadlines. This collaborative review helps refine understanding and processes.
- Seek Clarification for Unresolved Issues: If consensus cannot be reached between the original and IRR abstractor, submit questions to QualityNet for guidance and clarification.
- Apply Lessons Learned: Use insights from any mismatches to inform and improve future abstractions, ensuring continuous learning and enhancement.
- Analyze for Patterns: Regularly analyze results to identify trends or patterns in mismatches. This helps determine if additional IRR assessments or targeted staff education is necessary to maintain data accuracy.
Outsourcing IRR Assessments for Optimal Results
While conducting IRR in-house is beneficial, it may not always yield unbiased results. Outsourcing this process to an independent third-party, like American Data Network, ensures neutrality. Our experts provide IRR services that help your facility achieve accurate, reliable data and meet regulatory requirements. For a complete guide on IRR outsourcing, visit our inter rater reliability guide.
Get a Free Quote: Interested in improving your hospital’s Inter-Rater Reliability? Reach out for a free quote on how our services can support your quality initiatives. To learn more about our full range of data abstraction services, visit our data abstraction page.





