As the U.S. healthcare system continues its shift toward value-based care, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) is raising the stakes by making patient-reported outcomes a critical component of quality measurement. For hospitals performing elective total hip arthroplasty (THA) and total knee arthroplasty (TKA), this effort takes shape in the THA/TKA PRO-PM (Patient-Reported Outcome Performance Measure)—a program with significant operational challenges and financial implications. With mandatory data collection and reporting well underway, hospitals must navigate complex workflows, including tracking patients for up to a year post-surgery and ensuring they complete both pre- and post-op surveys.
For Directors and VPs of Quality, this measure requires more than just a data-collection system. It demands strategic planning, rigorous follow-up, and solutions to overcome a key hurdle: patients are typically off-site when the critical 300–425-day post-op survey window arrives. Without a structured follow-up process—through calls, emails, text reminders, or patient portals—hospitals risk falling short of the required 50% completion rate. Below, we highlight essential timelines, compliance requirements, and best practices to help you meet the demands of this evolving measure and protect your organization’s performance under CMS’s value-based initiatives.

1. Understanding the THA/TKA PRO-PM
Why PROMs for Hip and Knee Surgery?
- Direct Patient Voice: Traditional measures (e.g., complications, readmissions) capture clinical data, whereas patient-reported outcomes highlight how individuals perceive their pain, mobility, and overall quality of life.
- Quality Improvement: By comparing pre- and post-op survey scores, hospitals can evaluate the effectiveness of surgical interventions, fine-tune rehabilitation, and identify areas that need enhancement.
- Alignment with Value-Based Care: The CMS THA/TKA PRO-PM reflects CMS’s broader move toward patient-centered metrics that could influence reimbursement and public reporting.
2. Key Timeframes: Mandatory
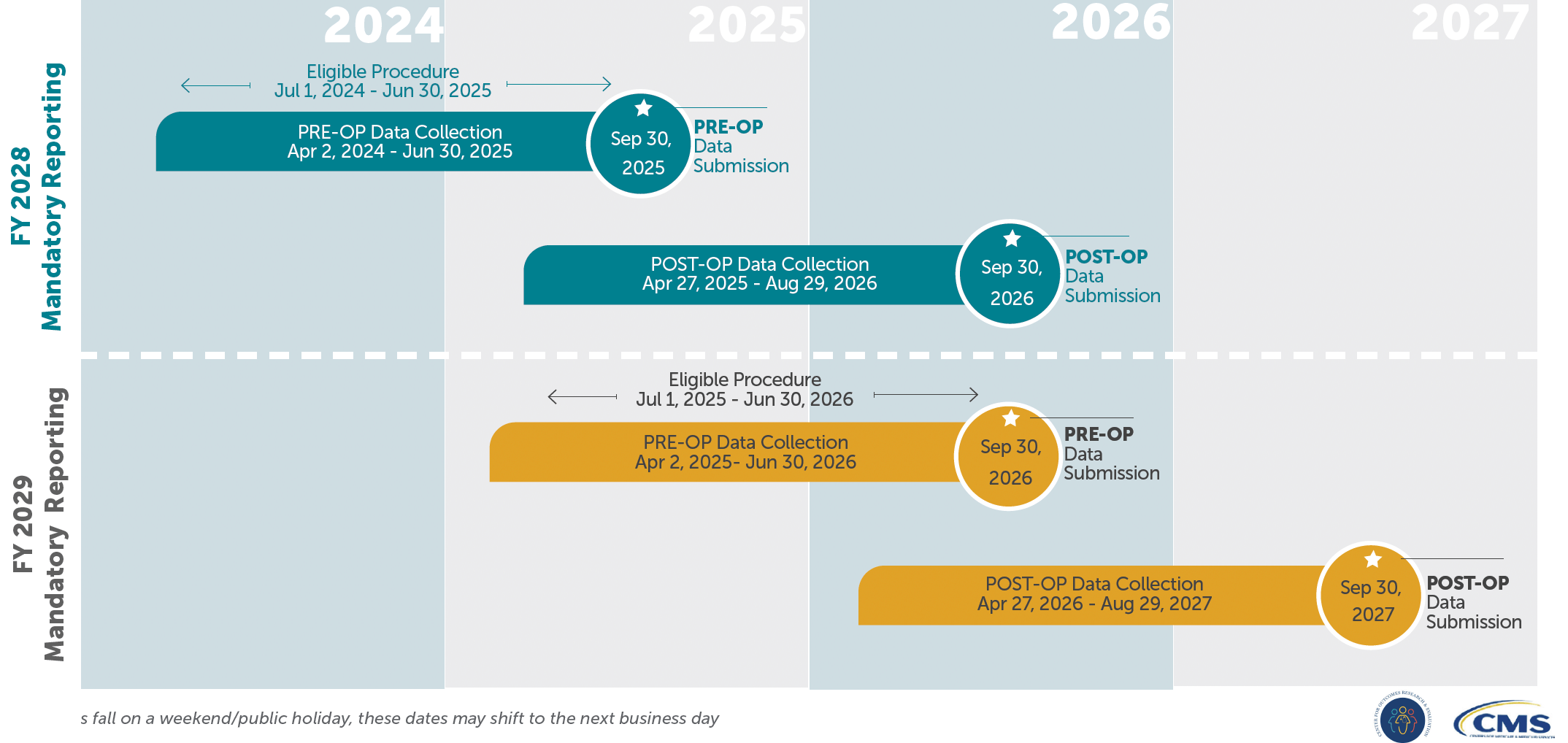
Pre-Operative Data Collection Windows
- Mandatory Period 1
- Data Collection: April 2, 2024 – June 30, 2025
- THA/TKA Procedures Performed: July 1, 2024 – June 30, 2025
- Submission Deadline: September 30, 2025
- Mandatory Period 2
- Data Collection: April 2, 2025 – June 30, 2026
- THA/TKA Procedures Performed: July 1, 2025 – June 30, 2026
- Submission Deadline: September 30, 2026
During the pre-operative window, patients must complete the THA/TKA PRO-PM survey 0–90 days before the surgery date.
Post-Operative Data Collection Windows
- Mandatory Period 1
- Data Collection: April 27, 2025 – August 29, 2026
- Submission Deadline: September 30, 2026
- Mandatory Period 2
- Data Collection: April 27, 2026 – August 29, 2027
- Submission Deadline: September 30, 2027
For each pre-op cohort, the post-op portion of the CMS THA/TKA PRO-PM occurs 300–425 days following the procedure. For instance, for surgeries performed in the first mandatory cycle (July 1, 2024 – June 30, 2025), post-op data collection begins April 27, 2025, with a submission deadline of September 30, 2026.

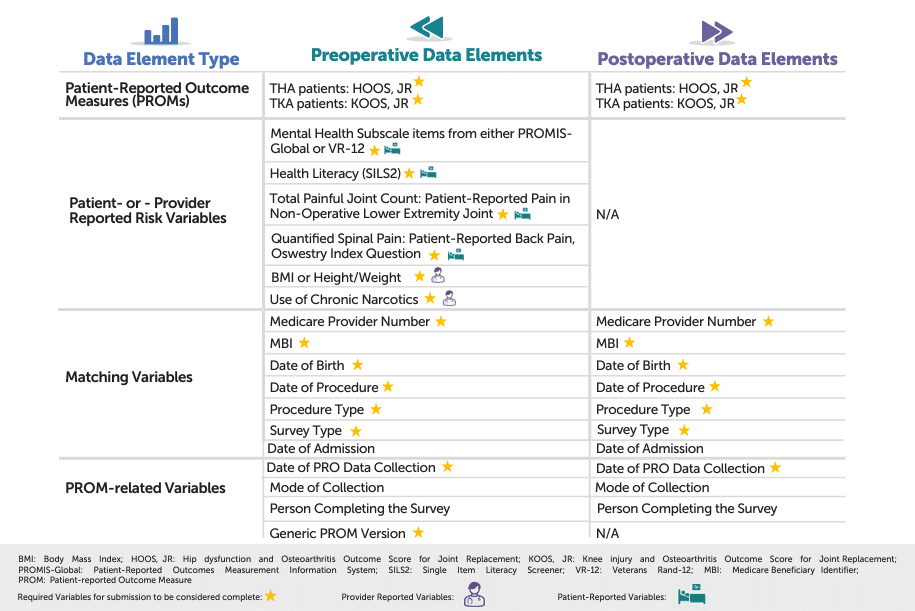
3. What THA/TKA PRO-PM Data Do I Collect?
Before your hospital can submit performance data for the THA/TKA PRO-PM, you need to capture both preoperative and postoperative patient-reported outcomes (PROs)—along with key risk variables and matching information. These data elements enable CMS to:
- Link Survey Responses to Administrative Claims – Ensuring each patient’s outcome can be accurately identified and attributed.
- Calculate a Risk-Adjusted Score – Factoring in patient characteristics (e.g., comorbidities, health literacy) so hospitals that serve more complex populations are measured fairly.
The graphic below outlines the primary categories of information you’ll be gathering—ranging from HOOS Jr. or KOOS Jr. functional scores to patient-provider reported risk factors such as BMI, mental health subscales, and narcotic use. By collecting the right data points at the right times (pre-op and post-op), your hospital can maximize response rates, ensure data integrity, and demonstrate meaningful, risk-adjusted improvements in hip and knee arthroplasty.
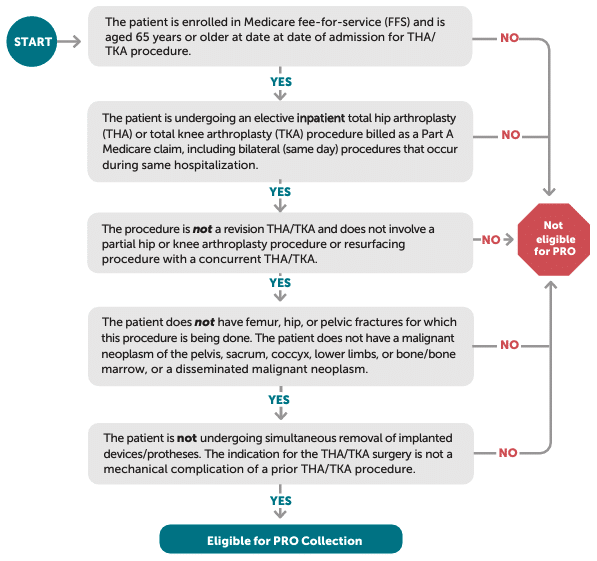
4. Who Do I Collect THA/TKA PRO-PM Data On?
Before you can measure improvement in hip or knee function, you need to identify which patients fall within the THA/TKA PRO-PM’s eligibility criteria. As illustrated in the figure, CMS requires that patients be 65 or older, enrolled in Medicare fee-for-service (FFS), and undergoing an elective inpatient primary THA or TKA procedure (rather than a revision or partial arthroplasty). The guidelines also exclude patients with hip fractures, active malignancies in the surgical site, or simultaneous device removal. By focusing on this target population, your hospital ensures it captures the correct pre- and post-op patient-reported outcomes data—ultimately laying the groundwork for accurate, risk-adjusted performance measurement.
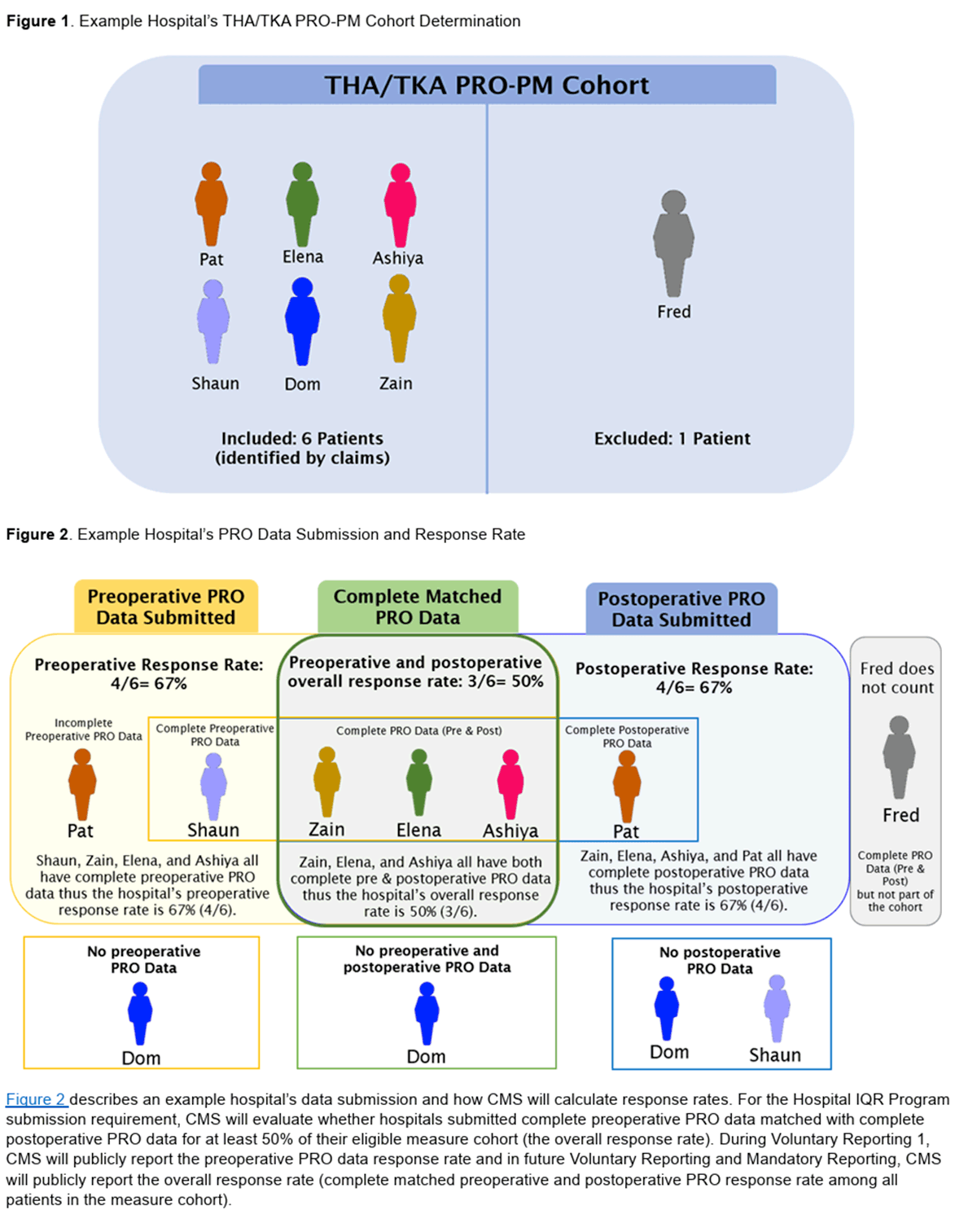
5. Meeting the 50% Completion Threshold
Under the THA/TKA PRO-PM, CMS requires hospitals to achieve at least 50% completion of matched pre- and post-op surveys. If a patient completes only one survey (pre or post), that case does NOT count toward compliance. The patient will also be excluded from the response rate if either the pre- or post-op survey is submitted as partial or incomplete.
Operational Implications
- Pre-Op Completion First: Missing the pre-op survey guarantees you cannot meet the target for that patient’s post-op.
- Post-Op Follow-Through: Patients are typically off-site when the 300–425-day postoperative window arrives. A structured follow-up process (calls, mail, text reminders, or portals) is crucial.
6. How THA/TKA PRO-PM Performance Will Be Scored
After navigating the data-collection timelines, matching at least 50% of your eligible patient population, and overcoming logistical hurdles, your hospital’s performance under the THA/TKA PRO-PM ultimately depends on how many patients meaningfully improve. In other words, CMS measures the percentage of patients whose self-reported scores indicate a “substantial clinical benefit” (SCB) one year post-surgery. Here’s how CMS calculates that percentage and why the right data-collection strategy is vitally important.
Defining the HOOS Jr. and KOOS Jr. Surveys
- HOOS Jr. (Hip disability and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score for Joint Replacement): A short-form questionnaire assessing hip-related pain, stiffness, and daily function.
- KOOS Jr. (Knee injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score for Joint Replacement): A parallel short-form survey focusing on knee pain, mobility, and activity limitations.
Each is scored on a 0–100 scale, with higher numbers indicating better function and/or less pain.
You can access both HOOS, JR. and KOOS, JR. survey forms here.
Substantial Clinical Benefit (SCB) Thresholds
CMS designates minimum point gains patients must achieve between pre-op (0–90 days before surgery) and post-op (300–425 days after surgery) to be considered improved:
- HOOS Jr.: 22-point improvement
- KOOS Jr.: 20-point improvement
If a patient’s post-op score rises by at least these amounts compared to their pre-op baseline, that patient’s outcome is classified as “substantial clinical benefit.”
Binary “Yes/No” Improvement
In practice, this means each patient’s result is categorized in one of two ways:
- Yes: The patient meets or exceeds the threshold for improvement (≥22 points on HOOS Jr. or ≥20 on KOOS Jr.).
- No: The patient does not meet that threshold.
Important: Patients must complete both a valid pre-op and a valid post-op survey to count toward your hospital’s measure performance at all.
Risk Adjustment
Recognizing that different patient populations have varying levels of complexity, CMS applies a risk-adjustment model to even the playing field. Key risk factors—often drawn from administrative claims data—include:
- Comorbid conditions (e.g., diabetes, hypertension, obesity)
- Patient demographics (e.g., age, sex)
By standardizing for these risks, CMS ensures hospitals treating more complex patients aren’t unfairly penalized when calculating improvement rates.
Hospital-Level Risk-Standardized Improvement Rate (RSIR)
Once each patient’s outcome is flagged “Yes” or “No,” CMS aggregates these results into a hospital-level Risk-Standardized Improvement Rate (RSIR). In essence:
- Numerator: The number of patients (out of those who have both surveys) who meet the SCB threshold.
- Denominator: All eligible patients who completed pre- and post-op surveys at your hospital.
- Risk Adjustment: A statistical adjustment is applied to account for your patient mix.
The final RSIR is a percentage reflecting how effectively your hospital improves patient-reported pain and function, relative to the expected outcome for your patient population.
The Role of Non-Response
Because non-response bias can skew performance scores if certain patient groups are less likely to complete surveys, CMS employs methods (e.g., weighting) to adjust for differences between responders and non-responders. However, this cannot fully compensate for a low response rate—which underscores the need to meet or exceed the 50% completion requirement to produce the most accurate, representative scores.
Bottom Line
Your performance on the THA/TKA PRO-PM is ultimately determined by the proportion of your matched patients who see a 20- or 22-point jump in their KOOS Jr. or HOOS Jr. scores, once CMS accounts for risk factors. Achieving a high Risk-Standardized Improvement Rate (RSIR) demands consistent patient engagement before and after surgery—and it hinges on robust workflows that capture data from a significant portion of your THA/TKA population. By optimizing data collection and timely follow-up, your hospital can demonstrate true patient-centered outcomes and position itself for long-term success in value-based care.
7. How Should I Submit My THA/TKA PRO-PM Data?
Submitting THA/TKA PRO-PM data accurately is critical for compliance with CMS requirements. Hospitals can simplify this process by using a specialized reporting tool like ADN’s Core Measures Application, which streamlines data mapping, ensures accuracy, and reduces administrative burden. Leveraging this type of solution ensures your hospital meets all CMS specifications while freeing your team to focus on patient care and quality improvement. If you don’t use ADN’s Core Measures Application, you can also submit an XML or CSV or manually enter data in CMS’s Hospital Quality Reporting System.
8. Will My Results Be Made Public?
Yes, CMS may publish your hospital’s THA/TKA PRO-PM results on platforms like Care Compare to promote transparency and accountability. These public reports allow patients, providers, and payers to view hospital performance on critical quality measures, including how well you improve patient outcomes after joint replacement surgeries. Strong results can enhance your hospital’s reputation, attract more patients, and provide benchmarks for ongoing quality improvement. Public transparency underscores the importance of robust data collection and achieving high performance under the THA/TKA PRO-PM.
9. Workflow Challenges and Recommended Solutions
Scheduling & Patient Identification
- Challenge: The measure is procedure date-based, requiring early identification of patients.
- Solution: Coordinate closely with clinics, scheduling, perioperative nurses, and orthopedic coordinators. Maintain a real-time or daily report of upcoming elective THA/TKA procedures within the 90-day pre-op window. Encourage patients to complete the pre-op survey during the days leading up to surgery or, at the latest, upon arrival onsite as part of their admission forms to ensure compliance and minimize delays.
Post-Op Tracking
- Challenge: Collecting patient-reported outcome data nearly a year after surgery can be logistically complex, especially when patients are no longer onsite and may be hard to reach.
- Solution: Leverage automated outreach—such as text or email reminders—or consider partnering with a specialized survey and data collection vendor like ADN that seamlessly manages post-op follow-up. These third-party systems can offload the burden from hospital staff by sending timed reminders, capturing patient responses, and integrating data directly into your reporting platform. This approach helps ensure higher response rates and keeps your facility on track to meet CMS THA/TKA PRO-PM deadlines.
Ready to streamline your post-op data collection? Contact us to learn how partnering with a specialized vendor can simplify your THA/TKA PRO-PM workflow and bolster compliance.
Data Integration & Submission
- Challenge: Survey results often reside outside the primary EHR, and thus must be mapped to patient demographics, ICD codes, and procedure dates for the CMS THA/TKA PRO-PM submission.
- Solution: Adopt standardized data-exchange formats and consistent exports—whether you use SurveyMonkey, a custom form, or an in-house system. Alternatively, partner with a survey and data integration vendor (such as ADN) that seamlessly consolidates responses and aligns them with patient identifiers. This automated approach minimizes errors, reduces manual labor, and ensures your hospital stays submission-ready for every data cycle.
Ongoing Monitoring
- Challenge: Overlooking progress until the final month can result in suboptimal completion rates.
- Solution: Establish monthly or quarterly dashboards that track pre-op completions, post-op completions, and overall match rates. Early detection of shortfalls allows timely course corrections.
10. Strategic Considerations for Quality Leaders
In-House vs. Vendor Solutions
Before deciding whether to manage the CMS THA/TKA PRO-PM requirements internally, savvy hospital leaders often weigh the cost-benefit of hiring staff—considering benefits, taxes, and other overhead—versus partnering with a specialized vendor. Some organizations find it more cost-effective to engage an experienced partner that provides automated reminders, survey platforms, and streamlined data aggregation, freeing internal teams to focus on direct patient care rather than administrative tasks.
Resource Allocation
If you opt to handle THA/TKA patient outreach in-house, you should plan for additional staffing or reassigning roles, especially around the one-year post-op mark when contacting patients is most challenging. However, a strategic vendor partnership may eliminate the need for new full-time equivalents (FTEs), decreasing overhead costs while still maintaining a robust, compliant workflow.
Long-Term Readiness
CMS’s emphasis on patient-reported outcomes will likely broaden beyond THA/TKA to include other elective procedures. By building (or outsourcing) a scalable infrastructure now, your hospital gains a significant head start on adopting future PROMs or similar mandates.
Performance Improvement
Leverage pre- and post-op outcome data to fuel continuous quality improvement. Share insights with surgical, rehabilitation, and executive teams to pinpoint successful tactics and address performance gaps—ultimately improving both care quality and patient satisfaction.
11. The Future of Patient-Reported Outcome Measures
The CMS THA/TKA PRO-PM marks a significant transition from purely clinical or process-based metrics to patient-centered performance measures. This shift extends well beyond regulatory compliance; it speaks to how hospitals will structure care delivery, engage patients, and align with future value-based initiatives.
Yet, how you implement THA/TKA PROM requirements now will set the precedent for future outcomes measurement. If a hurried, under-resourced workflow is established—one that becomes “business as usual”—your team may experience status quo bias, making it difficult to pivot when additional PROMs are inevitably mandated. Organizational inertia can lead to inefficient processes that become baked into daily operations, creating unnecessary costs and staff burden in the long run.
Conversely, standing up a thoughtful, well-organized approach from the beginning helps:
- Avoid Legacy Pitfalls: A properly configured data-collection system can be easily expanded or adapted as new patient-reported measures come into play.
- Reinforce Culture: When leadership champions PROMs strategically, staff embrace these processes as core components of quality improvement, rather than “just another mandate.”
- Enhance Scalability: A robust infrastructure allows you to replicate successes for other service lines—cardiology, oncology, or beyond—where patient-reported outcomes may soon emerge.
- Maintain Organizational Agility: By not settling for a suboptimal “quick fix,” you position the hospital to respond quickly to evolving CMS requirements, payer demands, and industry best practices.
Hospitals proficient in capturing, analyzing, and optimizing patient-reported outcomes through a solid initial framework not only fulfill CMS requirements but also build trust with patients, payers, and accreditation bodies. As future PROMs extend into additional service lines, early adopters with mature data-collection and analytics systems stand at a strategic advantage—ready to lead in patient-centered innovation rather than react to each new policy shift.
12. Essential Action Steps to Succeed with CMS THA/TKA PRO-PM
Implementing the CMS THA/TKA PRO-PM can seem daunting, especially as hospitals juggle timelines, staffing, and data integration. Yet, by focusing on the following practical measures, your organization can streamline workflow, strengthen compliance, and set a solid foundation for patient-reported outcomes in orthopedics—and beyond.
For Directors and VPs of Quality, the THA/TKA PRO-PM represents a key initiative that blends patient engagement with regulatory compliance:
- Confirm Timelines:
Pin down your hospital’s readiness for mandatory pre-op data collection (April 2, 2024 – June 30, 2025) and the corresponding post-op windows. Establish a clear internal schedule—across quality, perioperative, and IT teams—to ensure everyone understands key milestones and CMS submission deadlines. - Conduct a Workflow Gap Analysis:
Assess how patients are currently identified, surveyed, and tracked before and after surgery. Map out each step to pinpoint where data continuity might fail—such as missing handoffs between clinics, schedulers, and survey administrators—then assign responsibilities to ensure no gaps remain. - Invest in Monitoring Tools:
Implement a dashboard or tracking system that offers real-time insight into your pre-op and post-op completion rates. Regularly review these metrics with your team to spot trends early, correct workflow issues, and keep your 50% match goal well within reach. - Communicate the Value:
Reinforce with surgeons, nurses, and schedulers that comprehensive PROM data enhances quality metrics and patient satisfaction, and may soon influence reimbursement. By stressing future financial and public reporting stakes, you instill a shared sense of urgency and importance across all levels of care. - Plan for Growth:
Position your hospital for future PROM expansions beyond THA/TKA by designing a scalable process now. As CMS broadens patient-reported measures to new procedures, your well-honed infrastructure and engaged teams will translate to quick adoption and ongoing quality leadership.
By proactively focusing on these areas, your organization can fulfill CMS requirements for the THA/TKA PRO-PM and harness these insights to elevate orthopedic care quality—now and in the future.
Further Readings
QualityNet Website > THA/TKA PRO-PM Page
Official CMS portal containing measure specifications, timelines, and updates for the THA/TKA PRO-PM.
Link: https://qualitynet.cms.gov/inpatient/measures/THA_TKA
THA/TKA-PRO-PM FAQs (May 2024)
CMS document addressing common questions about the measure, including data collection and reporting requirements.
Link: https://qualitynet.cms.gov/files/66570e4e42e274bb6b8ca1cc?filename=THA_TKA-PRO-PM_2024_FAQ.pdf
Response Rate Requirement and Calculation
Guidance on how to measure response rates and meet CMS thresholds for the THA/TKA PRO-PM.
Link: https://qualitynet.cms.gov/files/6639270c2b87360fd3524bd7?filename=THA_TKA-PRO-PM_RspnsRateExpln.pdf
THA/TKA PRO-PM Overview Measure Fact Sheet
A concise fact sheet summarizing measure intent, scope, and key requirements.
Link: https://qualitynet.cms.gov/files/66390d2a2b87360fd3524a22?filename=THA_TKA-PRO-PM_FactSheet.pdf
What Data Should I Collect?
Detailed guidance on which data elements are essential for THA/TKA PRO-PM reporting.
Link: https://qualitynet.cms.gov/files/66fd8fb72702fb414b5455bc?filename=THA_TKA-PRO-PM_WhatData.pdf
Who Do I Collect PRO Data On?
Clarifies patient eligibility criteria for THA/TKA PROM collection.
Link: https://qualitynet.cms.gov/files/66390d8a2b87360fd3524a2d?filename=THA_TKA-PRO-PM_WhoCllctData.pdf
Hospital-Level THA/TKA PRO-PM Reporting Timeline
Outlines key dates and windows for data collection, post-op follow-up, and final submission.
Link: https://qualitynet.cms.gov/files/66390d67cc07c26dc848419c?filename=THA_TKA-PRO-PM_Timeline.pdf
Understanding THA/TKA PRO-PM Requirements (September 2023 Webinar)
Slide deck summarizing measure requirements, deadlines, and best practices from a CMS webinar.
Link: https://qualitynet.cms.gov/files/653926fae03c52001c055864?filename=THA-TKA_PRO-PM_Rqmts_Sept2023.pdf
THA/TKA PRO-PM Development Methodology Report
Explains the research and methodologies used in creating the THA/TKA PRO-PM.
Link: https://qualitynet.cms.gov/files/66fd8fa03e7d849a57e26b31?filename=THA_TKA-PRO-PM_MeasMthdlgy.pdf
2025 THA/TKA PRO-PM Code Specifications (VR1)
Inclusion and exclusion codes for the 2025 voluntary reporting cohort.
Link: https://qualitynet.cms.gov/files/66392124cc07c26dc8484302?filename=VR1_THA_TKA-PRO-PM-SplmntFile.xlsx
2026 THA/TKA PRO-PM Code Specifications (VR2)
Inclusion and exclusion codes for the 2026 voluntary reporting cohort.
Link: https://qualitynet.cms.gov/files/66a24e7ddf50d5628e69a997?filename=VR2_THA_TKA-PRO-PM-SplmntFile.xlsx
Comparison of THA/TKA PRO-PM in IQR, OQR, & ASCOR Programs
Fact sheet comparing how the THA/TKA PROM requirements apply across different CMS reporting programs.
Link: https://qualitynet.cms.gov/files/66390d57cc07c26dc8484196?filename=THA_TKA-PRO-PM_ProgCompFctsht.pdf
You may also like: